In English, time is not organized only by verb form. It is organized by how we see actions, facts, and moments. Before comparing present and past, we need to understand how English builds meaning step by step.
This text starts with the present, because it is the base. Then it moves to the past, and finally explains how English separates time clearly.
This explanation supports the main reference found in:📘 Present Perfect Explained: When English Connects the Past to the Present
The Present Tense: The Base Form in English
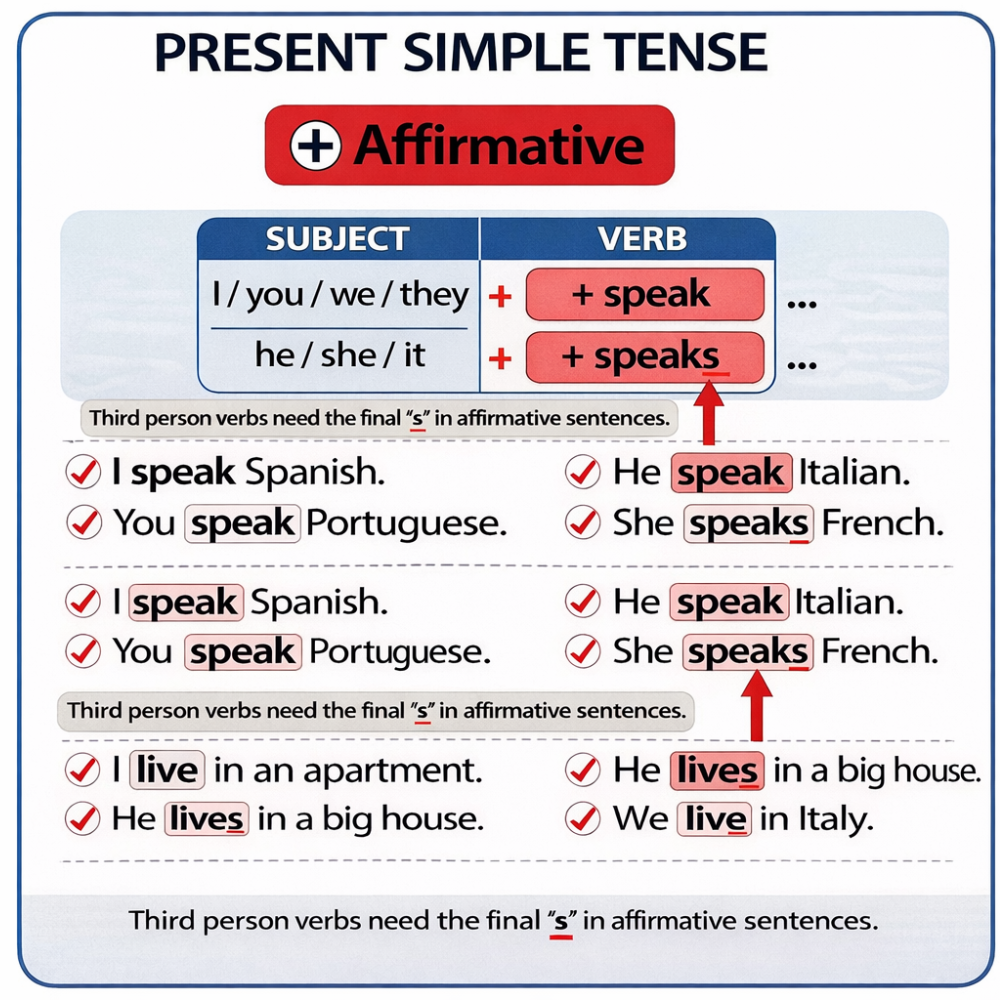
In English, the present simple is the base form of the verb.
We use it to talk about:
- routines
- habits
- things that are always true
- facts about the present
Example:
I work in London.
I read books every day.
I live near the city centre.
Here, the verb stays in its base form.
The Third Person: He, She, It
In English, something changes with the third person singular: he, she, it.
We add -s to the verb.
Examples:
She works in London.
He reads books every night.
She lives near the city centre.
This -s is one of the most important details in the present simple.
Present Simple Questions: Do and Does
In English, we use do and does to make questions in the present simple.
Examples:
Do you work in London?
Do they live nearby?
With he, she, it, we use does:
Does she work in London?
Does he read every day?
Notice something important:
When we use does, the verb goes back to the base form.
Does she work?
Not: Does she works?
Questions with Question Words
We often use do and does with question words.
Examples:
Where do you work?
What do you read?
When do they arrive?
With he, she, it:
Where does she work?
What does he do?
When does it start?
Questions with Who (No Do or Does)
In English, questions with who often do not use do or does, because who is the subject.
Examples:
Who lives here?
Who works in this office?
Who teaches English?
In these questions, who already replaces he or she.
Useful Everyday Present Simple Questions
| Question | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Where do you live? | place |
| What do you do? | job / activity |
| What time do you wake up? | routine |
| Do you work or study? | present situation |
| Does she live nearby? | third person |
These questions are very common in real conversations.
Present Simple Negatives
To make negative sentences in the present simple, we use do not or does not.
Examples:
I do not work on Sundays.
They do not live far from here.
With he, she, it:
She does not work on Sundays.
He does not live far from here.
Again, the verb stays in the base form.
Present Simple and Present Time
We use the present simple to talk about things that are true now.
Examples:
I am 19 years old.
My name is Daniel.
I live in Manchester.
She is a teacher.
These sentences describe facts, not actions in progress.
The Verb To Be in the Present
The verb to be is different. It does not use do or does.
Forms:
- I am
- you are
- he is / she is / it is
Examples:
I am tired.
She is at home.
They are students.
Questions:
Are you tired?
Is she at home?
Negatives:
I am not tired.
She is not at home.
Adverbs of Frequency and the Present Simple
We often use the present simple with adverbs of frequency.
Examples:
I usually wake up at 7.
She always drinks coffee in the morning.
We sometimes eat out.
These words show how often something happens.
Present Simple and Future Time
In English, we also use the present simple to talk about the future, especially with schedules and timetables.
Examples:
The train leaves at 6 a.m.
The class starts tomorrow.
The shop opens at 9.
Even though the time is future, English uses the present simple because the event is fixed.
Past Time: How English Talks About Finished Moments
Now we move to the past.
In English, the past simple is used when:
- the action is finished
- the time is finished
- the moment is clear
Examples:
I worked in London last year.
She read that book yesterday.
We met in 2022.
Words like yesterday, last week, in 2022 clearly place the action in the past.
The Key Difference Between Present and Past Time
The difference is not the verb form alone. It is the time perspective.
- Present time → habits, facts, routines, things true now
- Past time → finished actions at finished moments
English separates these two very clearly.
Understanding this organization helps everything else make sense, including the present perfect.
How This Connects to the Present Perfect
Once we understand how English separates present time and past time, it becomes easier to understand why English sometimes uses a tense that connects both.
That connection is explained in detail in📘 Present Perfect Explained: When English Connects the Past to the Present
Conclusion: English Time Is Organized, Not Random
In English, time follows a clear structure.
We start with:
- the present simple for facts and routines
- the past simple for finished moments
Only after that does English introduce tenses that connect time, such as the present perfect.
Once this foundation is clear, tense choice becomes logical, not confusing.
All content on Wilford Fluency is written and maintained by Márcio Wilford, an English teacher with over 10 years of experience. This article is provided for educational purposes only
Source: britishcouncil,