The present perfect is one of the most important verb tenses in English. At the same time, it is one of the most misunderstood, especially by students who already know basic grammar but still struggle with accuracy.
Many students learn formulas like have + past participle, but they do not fully understand why English uses this tense, when it is necessary, and how it relates to other tenses such as the past simple, past perfect, or present perfect continuous.
This page breaks down the present perfect and explains how English places events in time using this tense.
What the Present Perfect Really Expresses
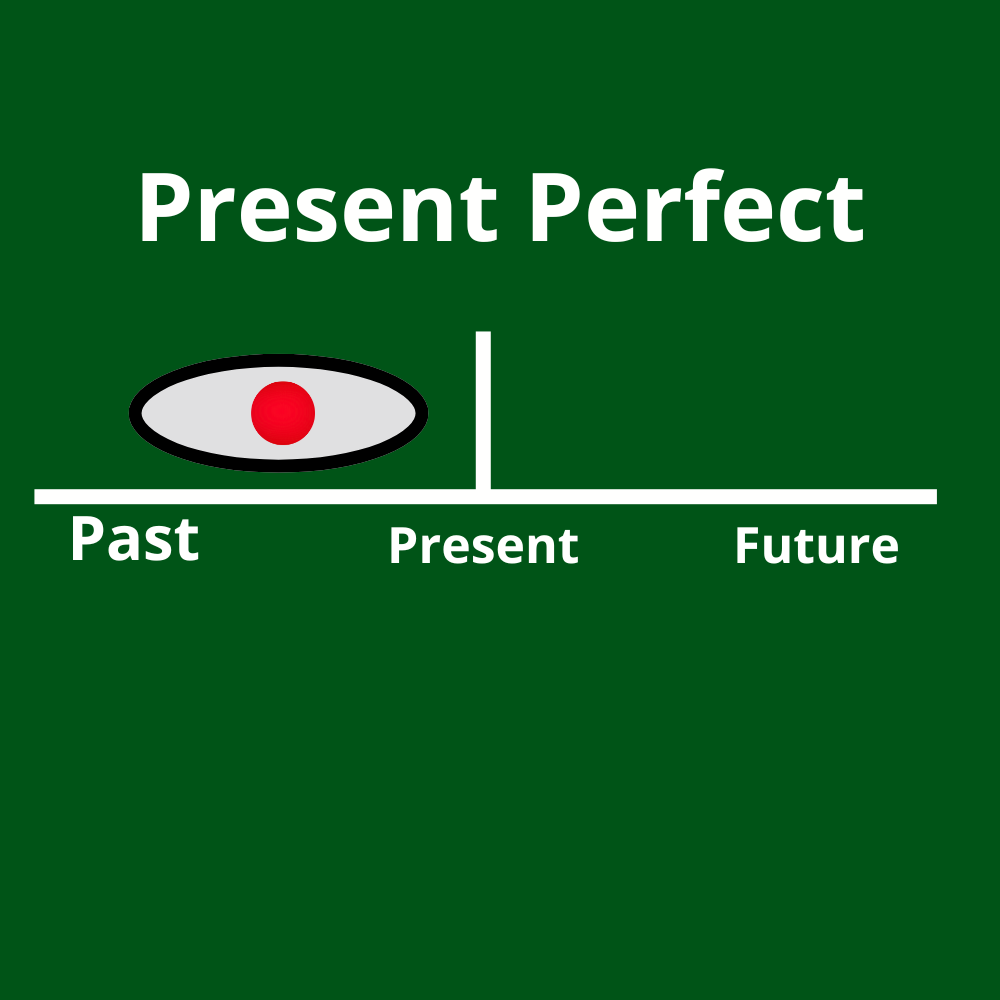
The present perfect is not about a finished moment in the past.
Instead, it describes a past action or state that is still relevant now.
English uses the present perfect when:
-
the exact time is not important
-
the result matters in the present
-
the situation continues until now
-
the experience itself is what matters
For example:
I have lost my keys.
The focus is not on when the keys were lost, but on the fact that they are still missing now.
How the Simple Present Perfect Is Formed and Used
The simple present perfect is formed with:
have / has + past participle
Examples:
I have finished the report.
She has never tried sushi.
We have seen this movie before.
In each case, a past action is connected to the present moment, either by result or experience. See also:
Irregular Verbs and the Present Perfect
When we use the present perfect, the verb form becomes especially important. That is because this tense is built with have / has + past participle, not with the simple past.
This is where irregular verbs often cause confusion.
In English, regular verbs form the past participle by adding -ed. However, irregular verbs do not follow a fixed pattern. Each irregular verb has its own past form and past participle, and these forms must be learned individually.
For example:
I have worked here for years.
I have seen this movie before.
She has gone home already.
In the present perfect and the past perfect, English always uses the past participle form of the verb. For regular verbs, this form looks familiar. For irregular verbs, it usually comes from the third column of irregular verb tables.
Because of that, understanding and memorizing irregular verbs is essential for using the present perfect accurately.
To see the most frequent irregular verbs used in real English and understand how their past participle forms work, see:
Since and For: Expressing Time Duration
One of the most common uses of the present perfect involves since and for, because this tense naturally works with time that continues until now.
Using Since
Since refers to a specific starting point.
I have lived here since 2019.
She has worked remotely since March.
The action started in the past and is still true now.
Using For
For refers to a period of time.
I have lived here for five years.
They have known each other for a long time.
The difference is not grammatical difficulty, but how time is framed. See more here:
Have Been vs Have Gone: Meaning and Presence
Learners often confuse have been and have gone, but the difference is logical.
Have Been
Means the person went somewhere and came back.
She has been to Paris twice.
She is not there now.
Have Gone
Means the person went somewhere and is still there.
She has gone to Paris.
She is not here now.
This distinction is essential because it tells the listener what is true at the present moment.
Present Perfect Continuous: Focus on Duration and Activity
The present perfect continuous emphasizes activity and duration, not just the final result.
Form:
have / has + been + verb-ing
Examples:
I have been studying all morning.
She has been working a lot lately.
Here, the focus is on what has been happening, not whether it is finished. See:
Present Perfect vs Present Perfect Continuous
Compare:
I have read the book.
The result matters. The book is finished.
I have been reading the book.
The activity matters. The book may not be finished.
Both tenses connect the past to the present, but they answer different questions. See more here:
Present Perfect with Adverbs (Ever, Never, Already, Yet, Just, Recently)
In English, certain adverbs and expressions frequently appear with the present perfect because they naturally express connection to the present without a finished time reference.
Understanding these words helps learners recognize when the present perfect is required.
Ever and Never: Life Experience
We use ever and never to talk about experience at any time up to now, without saying when something happened.
Have you ever visited Scotland?
I have never tried sushi.
The focus is not on time, but on whether the experience exists or not.
Already and Yet: Expectations and Completion
Already is usually used in affirmative sentences to show that something happened sooner than expected.
I have already finished the report.
Yet is common in questions and negative sentences to show that something has not happened up to now.
I haven’t finished yet.
Have you finished yet?
Both words naturally fit the present perfect because they look at the situation from the present perspective.
Just: Very Recent Actions
We use just with the present perfect to talk about something that happened a very short time ago, when the result is still important.
She has just left the office.
I’ve just received your message.
In this case, the exact moment is less important than the effect the action has right now
Recently and Lately: Near Past with Present Relevance
Recently and lately describe actions that happened in the near past, often repeatedly, with a clear connection to now.
I have been very busy lately.
She has worked from home recently.
These expressions often appear with the present perfect or the present perfect continuous.
Present Perfect vs Simple Present
The simple present describes facts, routines, and habits.
I work from home.
She teaches English.
The present perfect shows duration or experience that started in the past.
Compare:
I work from home.
This describes a routine.
I have worked from home for three years.
This shows how long the situation has existed.
Present Perfect vs Simple Present
The simple present describes facts, routines, and habits.
I work from home.
The present perfect shows duration or experience that started in the past.
I have worked from home for three years. See more:
Present Perfect vs Past Simple
This contrast is one of the most important in English.
- Present Perfect focuses on time up to now
- Past Simple focuses on a finished moment in the past
I have been here for twenty minutes.
I arrived here twenty minutes ago.
Past Perfect: Ordering the Past
The past perfect is used when English needs to talk about two situations in the past, where one happened before the other.
I had finished the report before the meeting started.
Both actions are in the past.
The past perfect marks the older action.
Present Perfect vs Past Perfect
This difference depends on the reference point. 📘 Present Perfect vs Past Perfect: Understanding Time Order
I have finished the report.
The result matters now.
I had finished the report before she arrived.
Both actions are completed and located in the past.
The present perfect connects past to now.
The past perfect organizes past events among themselves.
Past Perfect Continuous and Past Continuous (Overview)
English also uses continuous forms to describe ongoing past actions.
-
Past continuous shows an action in progress at a specific past moment
-
Past perfect continuous shows an ongoing action that happened before another past event
I was studying when she called.
I had been studying for hours before she called.
These tenses help clarify duration and sequence in the past.
Present and Past Time: The Big Picture
English organizes time using reference points:
-
Present tenses look toward now
-
Past tenses locate actions at fixed points in the past
-
Perfect tenses connect actions across time
When we understand this logic, choosing the correct tense becomes natural
Frequent Mistakes Students Make with the Present Perfect
One reason the present perfect feels difficult is that students often use other tenses without realizing what information they are giving to the listener.
A very common pattern happens with the past simple.
Mistake 1: Giving Information That Invites a “When?” Question
When a student says:
❌ I saw him.
This sentence is grammatically correct, but it immediately invites a question:
When did you see him?
By choosing the past simple, the speaker suggests that the time of the action matters, even if they do not mention it.
However, in many situations, the speaker does not want to talk about time.
Compare:
✅ I have seen him.
Now the listener understands that:
-
the experience matters
-
the exact time is not important
-
there is no need to ask when
Mistake 2: Using Past Simple When the Result Matters Now
Another very common example:
❌ I broke my arm.
This sentence almost automatically leads to the question:
When did it happen?
The focus is on a finished event in the past.
But if the speaker’s intention is to explain a current situation, English naturally prefers the present perfect:
✅ I have broken my arm.
Now the meaning is different:
-
the arm is still broken
-
the present condition matters
-
the time is secondary or irrelevant
This is exactly the type of situation where English chooses the present perfect.
Mistake 3: Using the Present Perfect with Finished Time Expressions
Students also frequently say:
❌ I have seen him yesterday.
This sounds wrong because yesterday already defines a finished moment in the past.
Correct version:
✅ I saw him yesterday.
Finished time expressions push English toward the past simple, not the present perfect.
Why These Mistakes Happen
These mistakes are not about verb forms. They happen because students:
-
think only about grammar rules
-
do not think about the listener’s expectations
-
translate directly from their first language
English tense choice is strongly connected to what information the speaker wants to highlight.
How to Think Correctly About the Present Perfect
Instead of memorizing rules, ask yourself:
-
Is the exact time important?
-
Does this action affect the present?
-
Does the situation continue until now?
If the answer is yes, the present perfect is usually the right choice.
Conclusion: Present Perfect Is About Connection
The present perfect is not complicated. It is simply English’s way of connecting the past to the present.
Once this logic is clear, contrasts with other tenses such as past simple, past perfect, and present perfect continuous become easier to understand and apply.
This page serves as a central reference for all topics related to the present perfect. From here, each concept can be explored in depth through focused articles that expand one idea at a time.
Mastering the present perfect will significantly improve your clarity, confidence, and naturalness in English.
Past Perfect Continuous: Duration Before Another Past Moment
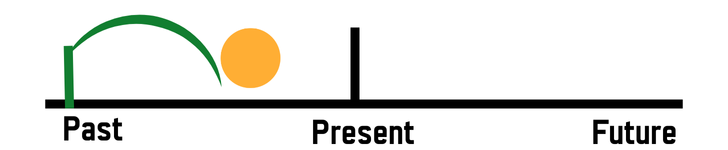
The past perfect continuous is used when English needs to show that an action started in the past and continued until another moment in the past. In other words, it describes duration before a second past event.
This tense is especially useful when the speaker wants to highlight how long something had been happening before it stopped or was interrupted.
Form
The past perfect continuous is formed with:
had + been + verb-ing
Examples:
She had been waiting for hours when the train finally arrived.
They had been working together for years before the company closed.
Questions and negatives follow the same logic:
Had you been studying long before the exam started?
He had not been sleeping well before the trip.
How It Works in Meaning
The key idea is time order inside the past.
The action:
- started earlier
- includes duration
- ended before another past event
Compare:
I had been driving for three hours when the car broke down.
The focus is not only on the breakdown, but on the long activity leading up to it.
This logic is similar to the present perfect continuous, but the reference point is another past moment, not now.
When English Chooses This Tense
English commonly uses the past perfect continuous when:
- the duration explains a past result
- the speaker wants to emphasize effort or activity
- one past situation helps explain another
For example:
She was exhausted because she had been working all day.
The tiredness makes sense because of the previous ongoing action.
Source: Englishpage, todamateria, britishcouncil